二、Nginx原来是这样?(系列篇02)
大家好,我是秋意零。
今天分享Nginx系列篇的第二节。Nginx目录结构、运行原理、基本配置。
更多请关注,Nginx系列篇主页:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/mp/appmsgalbum?__biz=Mzg3OTc2OTE3NA==&action=getalbum&album_id=3438641450349625348#wechat_redirect
目录结构
1)目录带有temp的字段是临时文件,是Nginx运行之后产生的。
❝
带有
temp目录的项在Nginx的目录结构中主要用于存储临时文件,这些目录与Nginx处理不同类型的请求时产生的临时数据相关。每个temp目录对应于Nginx处理特定类型请求时的临时存储需求,具体说明如下:
client_body_temp: 存储客户端请求体的临时文件。当客户端发送POST请求,且请求体较大时,Nginx会先将请求体写入到这个目录下的临时文件中,然后再由Nginx处理或转发给后端服务器。 fastcgi_temp: 用于FastCGI请求的临时文件存储。当Nginx作为前端服务器,与后端FastCGI应用服务器(如PHP-FPM)交互时,可能会需要存储一些临时数据,比如上传的文件或者大请求体。 proxy_temp: 服务于HTTP代理和反向代理请求的临时文件。当Nginx作为代理服务器转发请求到后端,并且需要暂存请求或响应的内容时,会用到这个目录。 scgi_temp 和 uwsgi_temp: 分别用于SCGI(Simple Common Gateway Interface)和uWSGI(Universal Web Server Gateway Interface)协议相关的临时文件存储。这两种协议类似于FastCGI,用于与不同的后端应用程序服务器通信。 这些临时文件夹的存在,使得Nginx能够高效处理各种类型的请求,尤其是在处理大数据量传输时,避免了直接在内存中存储大量数据,从而降低了系统内存的压力。需要注意的是,这些目录通常由Nginx服务运行的用户(如上面显示的
nobody)拥有权限,以确保安全性和隔离性。在生产环境中,定期清理这些临时文件是非常重要的维护操作,以避免磁盘空间被无用的临时文件耗尽。
[root@localhost nginx]# ll
total 0
drwx------ 2 nobody root 6 Apr 21 18:48 client_body_temp
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 333 Apr 21 18:24 conf # 配置文件目录
drwx------ 2 nobody root 6 Apr 21 18:48 fastcgi_temp
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 40 Apr 21 18:24 html # 静态资源目录
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 58 Apr 21 20:01 logs # 日志目录
drwx------ 2 nobody root 6 Apr 21 18:48 proxy_temp
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 19 Apr 21 18:24 sbin # 主程序目录
drwx------ 2 nobody root 6 Apr 21 18:48 scgi_temp
drwx------ 2 nobody root 6 Apr 21 18:48 uwsgi_temp
2)分别查看上诉目录内容
[root@localhost nginx]# ll conf/
total 68
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1077 Apr 21 18:24 fastcgi.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1077 Apr 21 18:24 fastcgi.conf.default
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1007 Apr 21 18:24 fastcgi_params
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1007 Apr 21 18:24 fastcgi_params.default
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2837 Apr 21 18:24 koi-utf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2223 Apr 21 18:24 koi-win
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5349 Apr 21 18:24 mime.types
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5349 Apr 21 18:24 mime.types.default
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2656 Apr 21 18:24 nginx.conf # 主要配置文件,该文件可以引用其它配置文件
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2656 Apr 21 18:24 nginx.conf.default
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 636 Apr 21 18:24 scgi_params
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 636 Apr 21 18:24 scgi_params.default
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 664 Apr 21 18:24 uwsgi_params
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 664 Apr 21 18:24 uwsgi_params.default
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3610 Apr 21 18:24 win-utf
[root@localhost nginx]# ll html/
total 8
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 497 Apr 21 18:24 50x.html # Nginx访问出现错误时的提示页面
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 615 Apr 21 18:24 index.html # Nginx默认访问的文件
[root@localhost nginx]# ll logs/
total 12
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1402 Apr 22 14:48 access.log # Nginx用户访问日志文件,所以访问都将记录在该文件中
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 648 Apr 22 14:48 error.log # Nginx访问报错时记录日志文件
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6 Apr 21 20:01 nginx.pid # 记录Nginx的主进程的Pid的文件
[root@localhost nginx]# ll sbin/
total 3804
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 3892104 Apr 21 18:24 nginx # Nginx程序启动文件
3)验证nginx.pid文件是否保存的主进程Pid
❝
可以看到nginx.pid文件内容,和nginx: master主进程ID一致。该文件为更具nginx: master主进程PID变化
[root@localhost nginx]# cat logs/nginx.pid
15032
[root@localhost nginx]# ps -aux | grep nginx
root 15032 0.0 0.0 20576 628 ? Ss 12:51 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
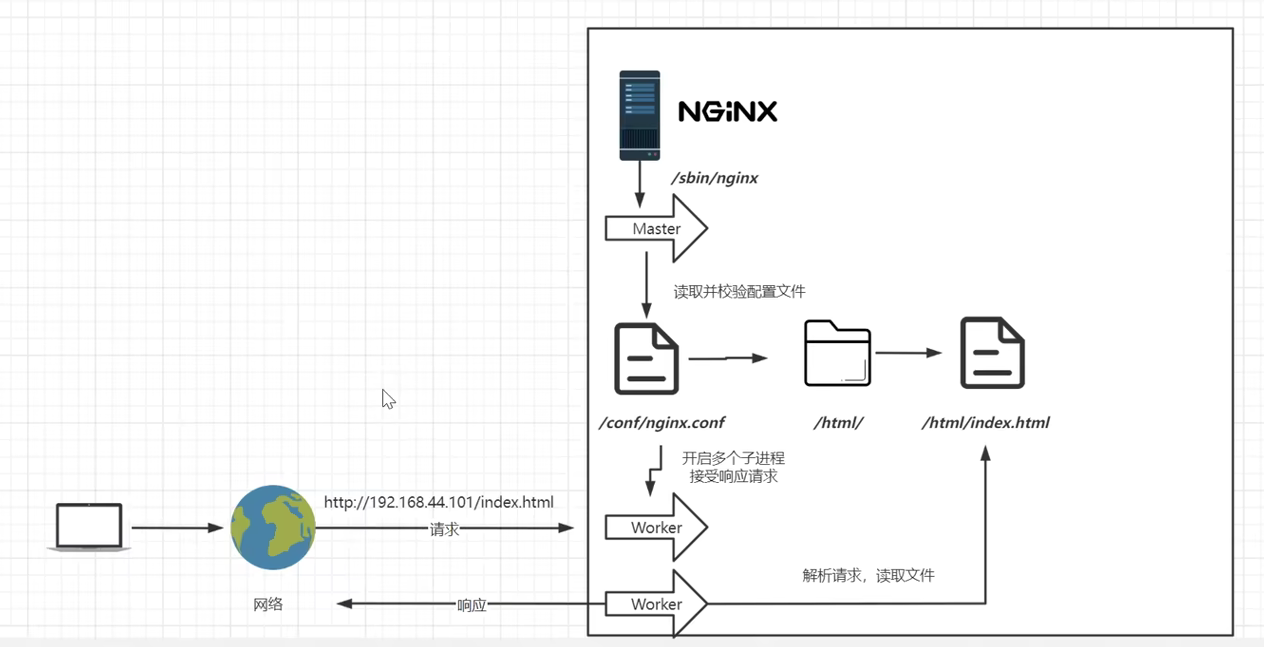
Nginx运行原理
1)主进程(Master Process)与工作进程(Worker Processes):
-
Master Process:Nginx 启动时,首先会生成一个主进程。主进程主要负责管理子进程、加载和验证配置文件、维护工作进程池,以及响应信号(如重新加载配置、优雅关闭等)。主进程不直接参与处理客户端请求。 -
Worker Processes:主进程会根据配置文件中指定的数量创建多个工作进程。每个工作进程都能够独立处理客户端的请求,包括接收请求、处理请求、返回响应等。工作进程数量通常与服务器的CPU核心数相匹配,以充分利用硬件资源。
❝
重新加载配置(reload操作):nginx.conf配置文件更改了,Master会将Worker进程Kill掉,Kill之前会留有一段时间让当前的Worker进程处理完手上的请求,不再接收新的请求了。Kill掉之后创建一个新的Worker进程,配置文件读取的也是最新的。
[root@localhost nginx]# ps -aux | grep nginx
root 15228 0.0 0.0 20576 620 ? Ss 14:56 0:00 nginx: master process ./sbin/nginx
nobody 15229 0.0 0.0 21020 1316 ? S 14:56 0:00 nginx: worker process
基础配置
1)初始配置文件(示例)
[root@localhost conf]# cat nginx.conf
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}2)Nginx配置各个区域块解析
-
全局块(Outside of any http{} block)
-
user: 指定运行 Nginx 工作进程的用户和组,默认为nobody或www-data。 -
worker_processes: 设置 Nginx 使用的工作进程数,通常与服务器的 CPU 核心数相匹配。 -
error_log: 定义全局错误日志的文件路径及日志级别。 -
pid: 设置 Nginx 主进程的 PID 文件路径。
-
-
Events Block
-
events { ... }: 控制 Nginx 如何处理连接。重要配置包括: -
worker_connections: 每个工作进程能同时打开的最大连接数。 -
use epoll(Linux): 指定使用的事件处理机制,如epoll提高性能。
-
-
-
HTTP Block
-
http { ... }: 包含了所有与 HTTP 协议相关的配置。 -
include mime.types: 引入 MIME 类型映射文件。 -
default_type application/octet-stream: 设定默认的 MIME 类型,用于未明确定义类型的文件。 -
log_format: 自定义日志格式。 -
access_log: 定义访问日志的文件路径及格式。 -
sendfile on;: 开启高效文件传输模式,减少 CPU 使用。 -
keepalive_timeout: 设置 Keep-Alive 连接超时时间。 -
server_tokens off;: 关闭服务器版本号在错误页面的显示,增强安全性。
-
-
-
Server Blocks
-
server { ... }: 定义一个虚拟主机或监听的端口配置。 -
listen 80;: 监听的端口号。 -
server_name example.com www.example.com;: 服务器名称,用于域名解析。 -
root /var/www/html;: 指定网站根目录。 -
location / { ... }: 定义不同URL路径的处理方式,如静态文件服务、反向代理等。 -
root html;:root指令指定了服务器根路径请求所对应的本地文件系统的根目录。在这个例子中,"html" 是一个目录名,它相对于 Nginx 安装目录(或在配置文件中通过alias指令指定的其他基路径)的相对路径。 -
index index.html index.htm;:index指令指定了当请求的URL是一个目录时,Nginx 应该优先尝试返回的默认文档列表。 -
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;: 尝试访问请求的文件或目录,如果找不到则返回404错误。 -
proxy_pass http://localhost:8000;: 如果是反向代理配置,则将请求转发给后端服务器。
-
-
这只是
nginx.conf文件中可能包含的部分配置示例。实际配置根据具体需求会更加复杂和多样化,可能还包括SSL证书配置、速率限制、缓存策略、Gzip压缩、rewrite规则等高级配置。每个配置指令的具体意义和可选参数,都可以在 Nginx 官方文档中找到详细的说明。Nginx 官方文档:https://nginx.org/en/docs/
-
❝
root和alias指令区别(面试题)
假设
root设置为/var/www/html,且location /images/处理图像请求,那么请求http://example.com/images/picture.jpg会映射到文件系统路径/var/www/html/images/picture.jpg。用户请求:http://example.com/images/picture.jpg 宿主机映射路径:/var/www/html/images/picture.jpg location /images { root /var/www/html; index index.html index.htm; }若使用
alias /var/www/html/在相同的location /images/中,同样的请求http://example.com/images/picture.jpg将直接映射到/var/www/html/picture.jpg,不会保留location中的/images/部分。用户请求:http://example.com/images/picture.jpg 宿主机映射路径:/var/www/html/picture.jpg location /images { alias /var/www/html/; index index.html index.htm; }详情参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/25093537
3)最小化Nginx配置文件,这里只是将注释去掉了。
[root@localhost conf]# cat nginx.conf
worker_processes 1; # worker进程启动数量
events {
worker_connections 1024; # 单个worker进程的连接数
}
http {
include mime.types; # include可以将其它配置文件引入到当前配置文件当中。mime.types文件是记录的请求头类型,比如:text/html、text/css、application/json请求头,打开文件查看详情。
default_type application/octet-stream; # 如果请求头类型,没在mime.types文件记录,那么就走default_type定义的application/octet-stream类型(格式流)
sendfile on; # 使用linux的sendfi1e(socket,file,1en)高效网络传输,也就是数据0拷贝。
keepalive_timeout 65; # 持久连接(Keep-Alive)的超时时间。当客户端与Nginx服务器之间启用HTTP Keep-Alive连接时,允许在一个TCP连接上连续发送多个HTTP请求,而不是为每个请求都新建一个TCP连接。这样可以减少建立新连接的开销,提高HTTP请求的效率。
# 一个server指一个虚拟主机 vhost
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost; # 指定主机的地址,可以是域名或IP
# location 用于根据客户端请求的URI(统一资源标识符)来匹配请求并执行相应的操作,如提供静态文件服务、代理请求到后端服务器、重定向等
location / {
root html; # root代表根目录,这里指的是/usr/local/nginx/html目录下
index index.html index.htm; # 默认访问的文件
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; # error_page指服务器端发生错误,比如返回500 502 503 504时,跳转到/50x.html文件。http://qiuyl.com/50x.html,但是上面的location /默认没有指定该文件,所以下面的location = /50x.html 判断后会在html目录找该文件。
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
End
非特殊说明,本博所有文章均为博主原创。
如若转载,请注明出处:https://www.qiuyl.com/nginx-xilie/178







共有 0 条评论